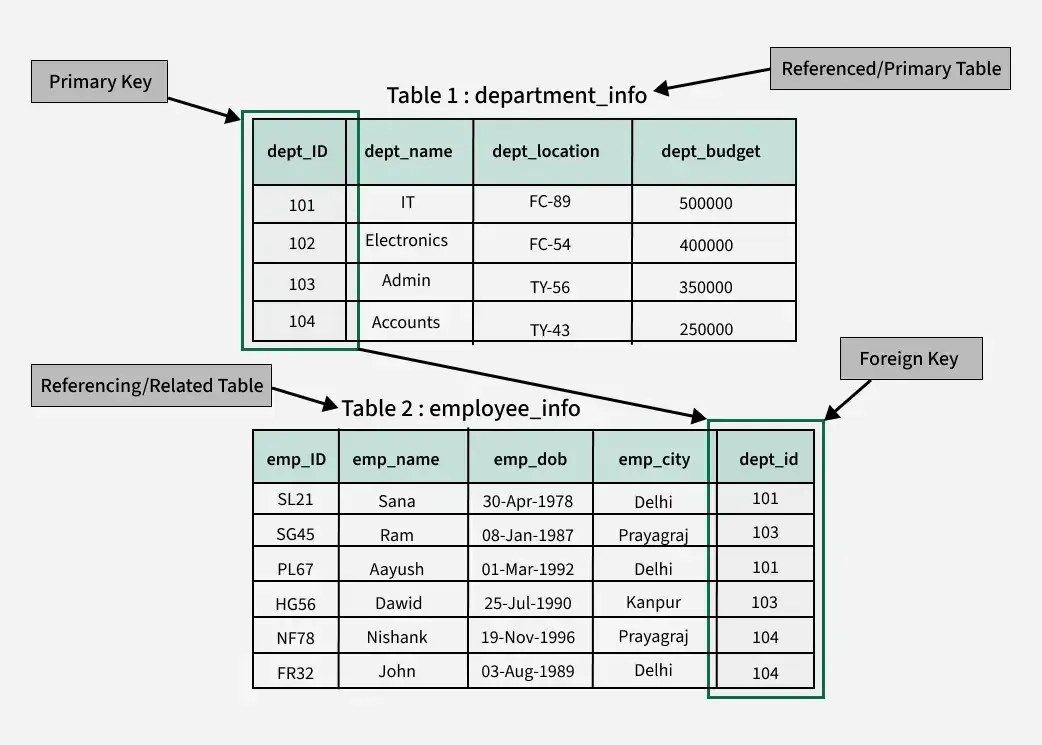
🔶 1. What is the Relational Model?
Definition
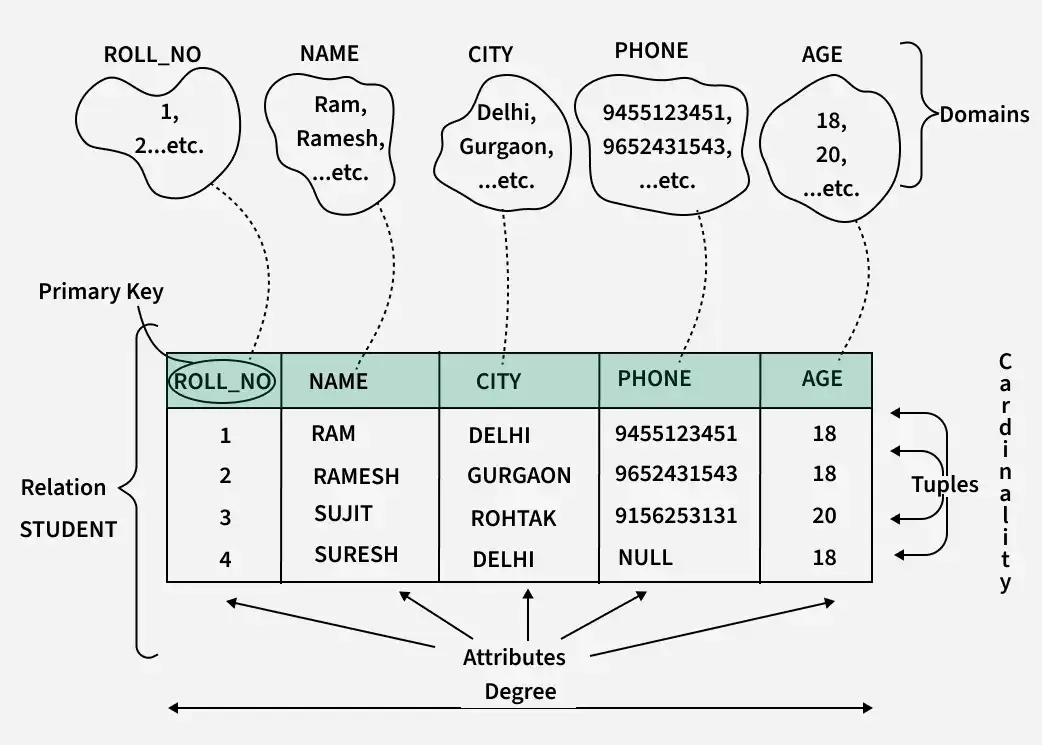
The Relational Model is a way to store and manage data in tabular form. It was introduced by E.F. Codd in 1970.
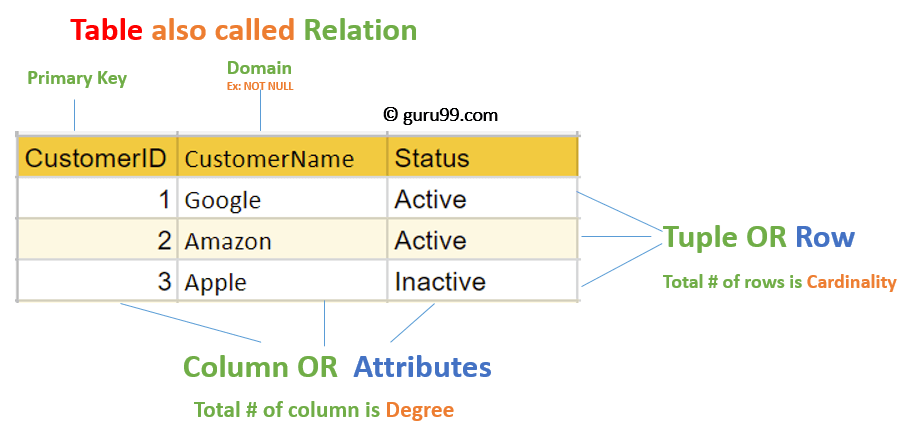
- Data is stored in Relations (Tables)
- Each row = Tuple (Record)
- Each column = Attribute (Field)
- Each column has values from a Domain (Allowed values)
📌 Real-World Analogy: College Record System
| Roll_No | Name (only allowed String → Domain) | Age (only allowed Integer → Domain) | Course_ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | Ravi | 20 | C101 |
| 102 | Meena | 21 | C102 |
- Table = "Student"
- Each row = 1 student → Tuple
- Each column → Attribute
- Age column only allows integers → Domain
📌 MySQL Datatypes with Example & Use Case
-- Creating the Student table with MySQL datatypes
CREATE TABLE Student (
Roll_No INT PRIMARY KEY, -- INT → Numeric values (e.g., 101, 102)
Name VARCHAR(50), -- VARCHAR → Variable length string (e.g., 'Ravi')
Age INT CHECK (Age >= 18), -- INT → Only whole numbers (e.g., 20)
Course_ID CHAR(5), -- CHAR → Fixed length string (e.g., 'C101')
DOB DATE, -- DATE → Stored in 'YYYY-MM-DD' format
Admission_Date DATETIME, -- DATETIME → 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS'
Remarks TEXT -- TEXT → Long text storage (not CLOB in MySQL)
);
🔹 Common MySQL Datatypes & Use Cases
- INT → Whole numbers (e.g., Roll_No, Age, Salary, Quantity)
- VARCHAR(n) → Variable-length text (e.g., Names, Emails, Addresses)
- CHAR(n) → Fixed-length text (e.g., Course_ID, Gender 'M/F')
- DATE → Stores only date in
'YYYY-MM-DD'(e.g., '2025-10-01') - DATETIME → Stores date & time in
'YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS' - TIMESTAMP → Auto-updated time values (useful for Created_At, Updated_At)
- DECIMAL(p,s) → Exact decimals (e.g., Price DECIMAL(10,2) → 99999999.99)
- BOOLEAN (alias of TINYINT(1)) → True/False values
- TEXT → Long character text (e.g., Remarks, Description) ✅ replaces CLOB
- BLOB → Binary data (e.g., Images, PDF files)