🧠 DBMS Normalization - Complete Guide
✅ What is Normalization?
Normalization is the process of organizing data in a database to reduce redundancy and improve data integrity. It involves dividing large tables into smaller ones and defining relationships between them.
It helps to:
- Eliminate duplicate data
- Ensure data dependencies make sense
- Make the database more efficient and easier to maintain
📚 Example:
Without Normalization:
| Student_ID | Student_Name | Subject1 | Subject2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | Ram | Math | Science |
| 102 | Riya | Math | English |
| 101 | Ram | Math | Science |
🔁 Here, Ram is repeated. It wastes space and can cause errors.row level redundancy removes by primary key make student as primary key
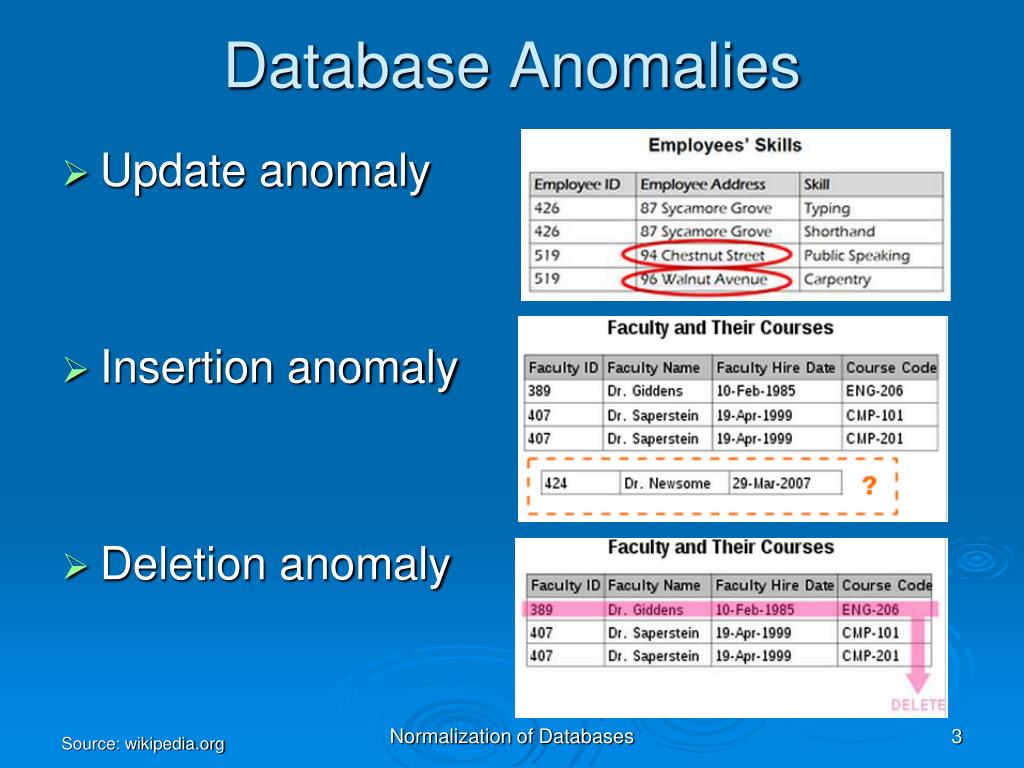
🧐 Why Normalization?
To avoid:
-
Update Anomaly: If we update a value in one place and forget to update in other
places.
Example: A customer's phone number is stored in 3 different places. If the number changes and only 2 are updated, the data becomes inconsistent. -
Insert Anomaly: We can't insert data unless some other data exists.
Example: We can't add a new course unless we already have a student enrolled in it, because both course and student are stored in the same table. -
Delete Anomaly: Deleting data removes useful info unintentionally.
Example: If we delete the last student enrolled in a course, the course data also gets deleted, even though the course still exists.
🔶 Types of Normal Forms
🥇 1NF – First Normal Form
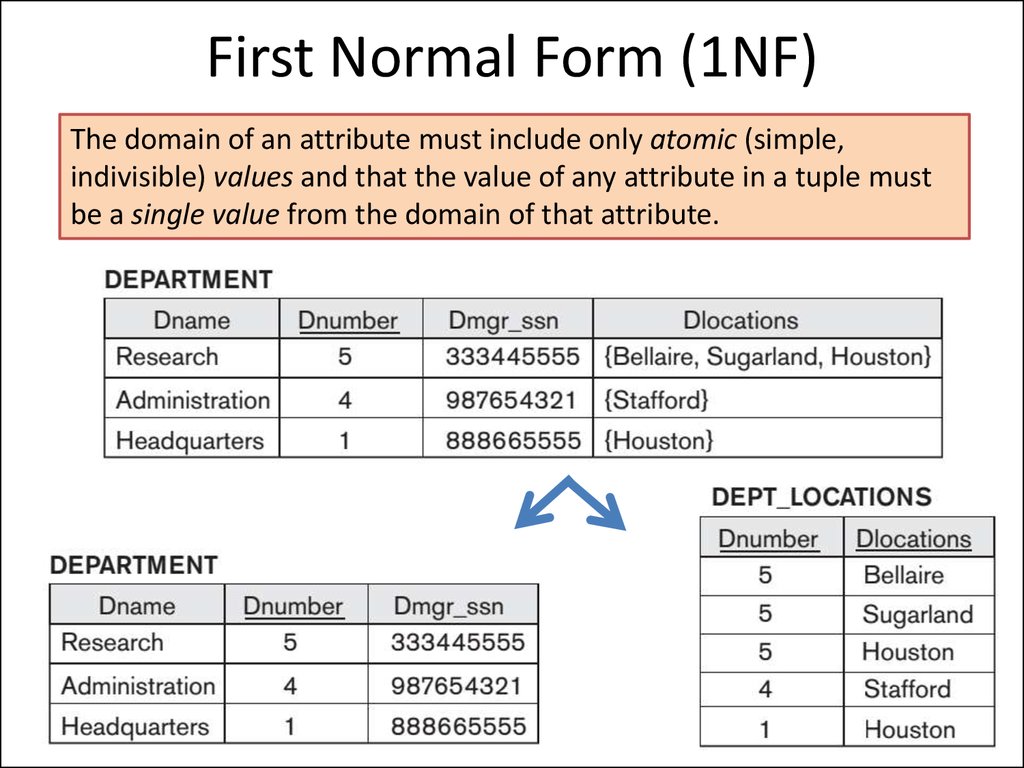
Rule:
- Each cell should have a single value (no multiple values).
- Each row must be unique.
📌 Bad Table (Not in 1NF):
| Roll | Name | Subjects |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amit | Math, Science |
| 2 | Riya | English, History |
📌 Good Table (1NF):
| Roll | Name | Subject |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amit | Math |
| 1 | Amit | Science |
| 2 | Riya | English |
| 2 | Riya | History |
🗣 Interview Question:
Q: What is 1NF? Why is repeating groups bad in a table?
Answer:
1NF (First Normal Form) ensures that each column in a table contains only **atomic (indivisible)** values and each record is unique.
Repeating groups are bad because:
- They make it hard to query data efficiently.
- They lead to redundant and inconsistent data.
- They violate the rule of storing only one value per cell.
Example:
❌ Not in 1NF (Repeating groups):
+------------+-----------------------+
| Student_ID | Subjects |
+------------+-----------------------+
| 101 | Math, English, Hindi |
+------------+-----------------------+
✅ In 1NF (Atomic values):
+------------+----------+
| Student_ID | Subject |
+------------+----------+
| 101 | Math |
| 101 | English |
| 101 | Hindi |
+------------+----------+
🥈 2NF – Second Normal Form
✅ Rule to be in 2NF:
- The table must already be in 1NF
- There should be no partial dependency
🤔 What is Partial Dependency?
If a table has a composite primary key (made from two or more columns), and a non-key column depends only on part of that key—not the whole— then it's a partial dependency.
🎓 Example Table: Student_Course
| Roll_No | Course_ID | Course_Name | Student_Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 101 | C01 | DBMS | Deepak |
| 101 | C02 | OS | Deepak |
| 102 | C01 | DBMS | Shreeram |
Primary Key: (Roll_No, Course_ID)
Partial Dependencies: Student_Name depends only on Roll_No, and Course_Name depends only on
Course_ID.
❌ This violates 2NF.
🛠 Converting to 2NF:
We split the table into three:
📘 Table 1: Student
| Roll_No | Student_Name |
|---|---|
| 101 | Deepak |
| 102 | Shreeram |
📗 Table 2: Course
| Course_ID | Course_Name |
|---|---|
| C01 | DBMS |
| C02 | OS |
📙 Table 3: Student_Course
| Roll_No | Course_ID |
|---|---|
| 101 | C01 |
| 101 | C02 |
| 102 | C01 |
✅ Now the design is in 2NF. All non-key columns fully depend on the full primary key.
🗣 Interview Tip:
Q: What is 2NF?
A: 2NF ensures that all non-key attributes are fully dependent on the entire primary
key. It removes partial dependencies from a table with a composite primary key.

🥉 3NF – Third Normal Form (Simple Explanation)
✅ Rules of 3NF:
- The table must already be in 2NF
- There should be no transitive dependency
🤔 What is Transitive Dependency?
Every column in the table should depend directly on the primary key.
If a column depends on another column (not on the primary key), that’s called a transitive
dependency.
🎓 Example (Bad Table – Not in 3NF)
| Roll | Name | Dept_ID | Dept_Name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amit | 10 | Computer |
| 2 | Riya | 20 | Electrical |
Problem: Dept_Name depends on Dept_ID, and Dept_ID
depends on Roll.
So Dept_Name is not directly dependent on the primary key
Roll.
This is called a transitive dependency ❌
If a table is not in 3NF:
- It may store the same data many times (data repetition).
- If department names change, we need to update many rows — this can lead to errors or inconsistent data.
- It increases data redundancy and wastes storage.
✅ Good Design – After Applying 3NF
📘 Student Table
| Roll | Name | Dept_ID |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Amit | 10 |
| 2 | Riya | 20 |
📗 Department Table
| Dept_ID | Dept_Name |
|---|---|
| 10 | Computer |
| 20 | Electrical |
✅ Now every column in the Student table depends only on the primary key Roll.
🎉 This design follows Third Normal Form (3NF)!
🗣 Interview Tip:
Q: What is Transitive Dependency?
A: It happens when a column depends on another column instead of directly on the
primary key.
Example: Dept_Name depends on Dept_ID, not on Roll.
🏆 BCNF – Boyce-Codd Normal Form
✅ Rules of BCNF:
- The table must be in 3NF
- For every dependency A → B, A should be a super key
🤔 What is a Super Key?
A super key is a column (or set of columns) that can uniquely identify each row in a table.
📌 Bad Table (Not in BCNF)
| Teacher | Subject | Dept |
|---|---|---|
| Ram | Math | Science |
| Ram | Physics | Science |
Issue: Teacher → Dept, but Teacher is not a super key.
This breaks the rule of BCNF.
❌ What happens if not in BCNF?
- Same department info is repeated for the same teacher (data redundancy)
- If the department changes, you must update it in many places (update problem)
- You may end up with mismatched or wrong data (inconsistency)
✅ Fix – Break into 2 Tables
📘 Teacher Table
| Teacher | Dept |
|---|---|
| Ram | Science |
📗 Subject Table
| Subject | Teacher |
|---|---|
| Math | Ram |
| Physics | Ram |
✅ Now every dependency follows the rule: the left side is a super key. This design is in BCNF.
🗣 Interview Question:
Q: What is the difference between 3NF and BCNF?
A: In 3NF, some non-super key dependencies are allowed. In BCNF, the left side of
every dependency must be a super key.
⭐ 4NF – Fourth Normal Form (Optional)
Rule:
- Must be in BCNF
- No multi-valued dependencies
A student can have multiple skills and multiple projects.
📌 Bad Table (Not in 4NF):
| Student | Skill | Project |
|---|---|---|
| Riya | Java | WebApp |
| Riya | C++ | WebApp |
| Riya | Java | GameDesign |
| Riya | C++ | GameDesign |
✅ Split into:
Skill Table:
| Student | Skill |
|---|---|
| Riya | Java |
| Riya | C++ |
Project Table:
| Student | Project |
|---|---|
| Riya | WebApp |
| Riya | GameDesign |
💎 5NF – Fifth Normal Form (Optional)
- Deals with join dependency
- Rare in practical use
📋 Normalization Forms – Quick Comparison
| Form | Rule | Main Focus | Problem It Solves | Example Issue |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1NF (First Normal Form) |
- Only atomic (single) values in each cell - No repeating groups or arrays |
Make each cell contain only one value | Removes multi-valued or repeated fields | A student has multiple phone numbers in one cell |
| 2NF (Second Normal Form) |
- Must be in 1NF - No partial dependency (non-key column depends only on part of composite key) |
Remove partial dependency | Solves redundancy caused by composite keys | Student_Name depends only on Roll_No, not full key (Roll_No, Course_ID) |
| 3NF (Third Normal Form) |
- Must be in 2NF - No transitive dependency (non-key depends on another non-key) |
Remove indirect dependency | Prevents update and inconsistency problems | Dept_Name depends on Dept_ID, not Roll directly |
| BCNF (Boyce-Codd Normal Form) |
- Must be in 3NF - Left side of every dependency must be a super key |
Stronger version of 3NF | Removes all anomalies where non-super key determines something | Teacher → Dept but Teacher is not a super key |
🧠 Quick Tip:
- 1NF: Remove repeating values
- 2NF: Remove partial dependency
- 3NF: Remove transitive dependency
- BCNF: Make sure all dependencies come from super keys
🔁 Denormalization
Sometimes, we combine tables back together to:
- Improve performance (less joins)
- Make querying faster
📌 Example:
Normalized (2 tables):
StudentCourse
Denormalized (1 table):
| Student | Course | Teacher |
|---|---|---|
| Riya | Math | Ram |
Denormalization increases redundancy but improves speed in some cases.
🗣 Interview Question:
What is denormalization? When do we use it?
📌 Quick Interview Questions Recap
- What is Normalization? Why is it needed?
- Explain 1NF, 2NF, 3NF with example tables.
- What is the difference between 3NF and BCNF?
- What are the anomalies in DBMS?
- When do you denormalize a database?

This HTML note is ready for easy revision and can be saved for offline use!