🔐 Encryption
Protects data from unauthorized users. Algorithms: AES-256, RSA, SHA.
VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology that creates a secure, encrypted connection over a public network (like the Internet) to another network (such as your company's internal network or a private server).
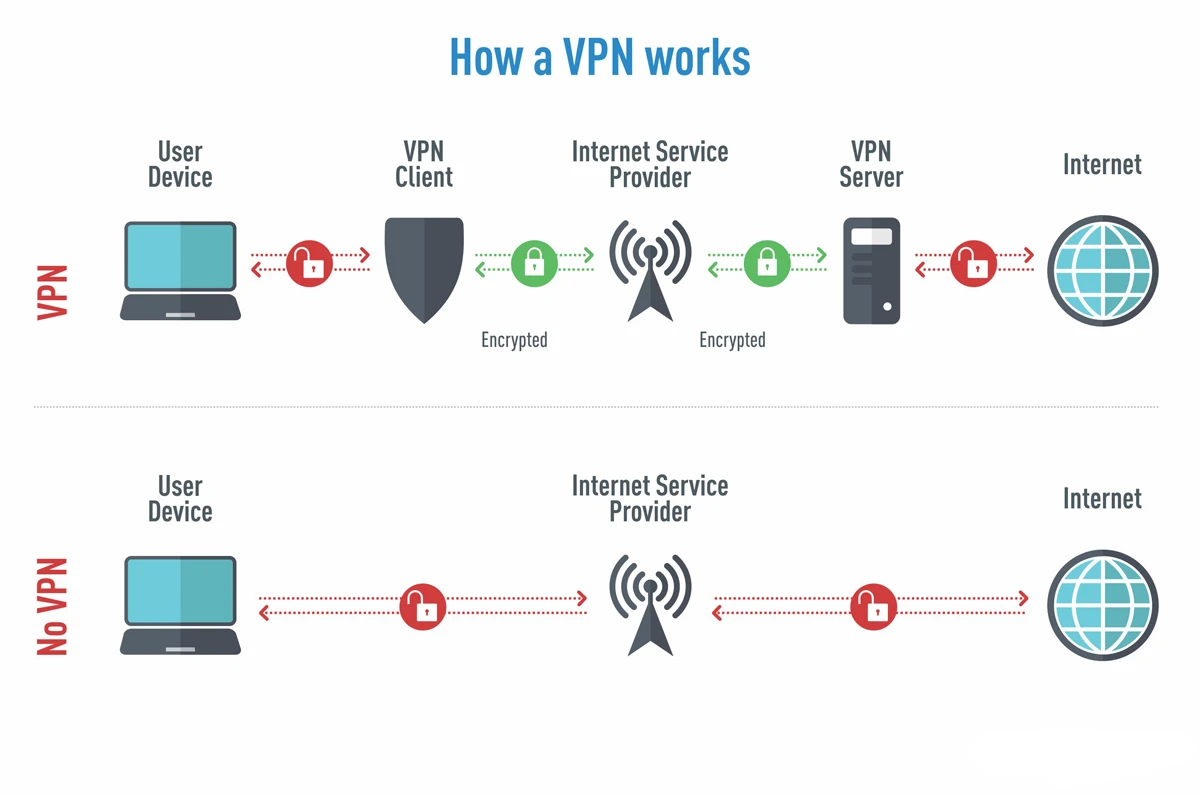
User (client) opens a VPN app and connects to a VPN server.
The VPN client authenticates with the VPN server using credentials (username/password, certificates, etc.).
A secure tunnel is established between the client and the server using protocols like:
All internet traffic from the user’s device is encrypted before leaving the device.
Encrypted data goes to the VPN server → decrypted → sent to the destination.
Data comes back to the VPN server → encrypted → sent to the client → decrypted.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| 🔒 Secure Public Wi-Fi | Protects data from hackers on public Wi-Fi. |
| 🌍 Bypass Geo-Restrictions | Access blocked sites (e.g., Netflix USA from India). |
| 👨💼 Remote Work | Secure access to company resources from home. |
| 🕵️♂️ Online Privacy | Hides your IP address and encrypts traffic. |
| 🚫 Bypass Censorship | Access restricted sites in censored countries. |
| 🏢 Site-to-Site VPN | Connects two office networks securely. |
| 🧪 Testing from Different Locations | Test websites from different regions. |
Protects data from unauthorized users. Algorithms: AES-256, RSA, SHA.
Encapsulate and encrypt data. Examples:
Replaces your real IP with server’s IP.
Cuts off internet if VPN drops.
Some traffic uses VPN; some goes direct.
| Feature | VPN | Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Yes | No |
| Anonymity | High | Low |
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Application | Entire device | Specific apps |