Networking Concepts for Interviews
1. VPN (Virtual Private Network)
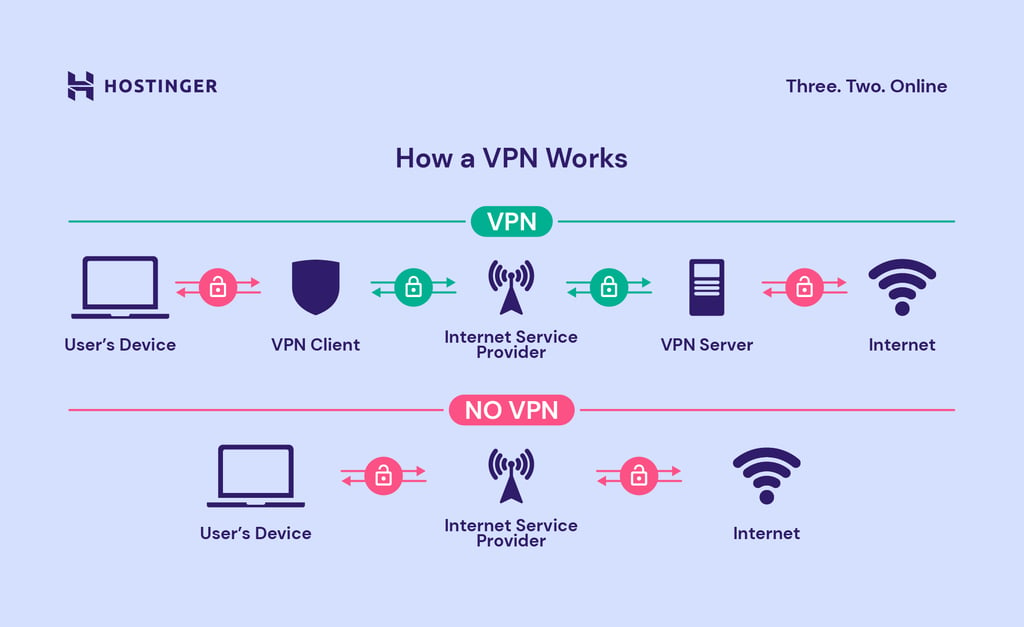
Definition: A secure tunnel for private communication over the internet.
Purpose: Protects data on public networks, enables remote access, bypasses geo-restrictions.
How it Works:
- Establishes a secure connection using protocols like OpenVPN, IPSec, or WireGuard.
- Encrypts data to prevent eavesdropping.
- Assigns a new IP address from the VPN server’s location.
Use Cases:
- Secure remote work.
- Bypassing censorship.
- Protecting data on public Wi-Fi.
Key Components:
- VPN Client: Software on the user’s device.
- VPN Server: Handles encryption and routing.
- Tunneling Protocol: Defines data encapsulation (e.g., PPTP, L2TP).
Interview Points:
- Protocols: OpenVPN (secure), IPSec (widely used), WireGuard (fast).
- Encryption: AES-256 standard.
- Split Tunneling: Selective traffic routing through VPN.
2. Firewall
Definition: A firewall is a security system (hardware, software, or both) that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined security rules. Think of it as a security guard for your network.
Purpose:
- Protects networks from unauthorized access, malware, and cyberattacks.
- Monitors network traffic to ensure only safe communication happens.
- Enforces security policies in organizations.
Why Firewalls are Needed:
- Prevent hackers from accessing private systems.
- Control which services or websites can be used.
- Stop malicious programs from sending data outside.
How a Firewall Works:
- Inspects each data packet that tries to enter or leave the network.
- Allows or blocks data based on rules (IP address, port number, protocol, application).
- Works at different OSI layers:
- Layer 3 (Network): Packet filtering based on IP addresses.
- Layer 4 (Transport): Filters based on TCP/UDP ports and connection state.
- Layer 7 (Application): Examines and filters actual application data like HTTP, FTP, etc.
Types of Firewalls:
- Packet-Filtering Firewall: Examines packet headers (source/destination IP, port, protocol). Simple but less secure.
- Stateful Inspection Firewall: Tracks the state of active connections, allowing only valid packets related to known connections.
- Application-Layer (Proxy) Firewall: Works as a middleman between user and the internet, filtering based on application data.
- Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW): Advanced features like Intrusion Detection System (IDS), Intrusion Prevention System (IPS), Deep Packet Inspection (DPI), and malware detection.
Firewall Modes:
- Whitelist Mode: Only traffic that matches allowed rules can pass; everything else is blocked.
- Blacklist Mode: Blocks only defined malicious or unwanted traffic; everything else is allowed.
Common Use Cases:
- Blocking access from suspicious IP addresses.
- Allowing only secure web traffic (HTTPS on port 443).
- Preventing unauthorized remote logins to servers.
Limitations:
- Cannot stop attacks from inside the network (insider threats).
- Cannot detect viruses hidden in allowed traffic unless integrated with antivirus.
- Cannot inspect encrypted traffic without SSL decryption enabled.
- Needs proper configuration; wrong rules can create security holes.
Important Interview Points:
- Difference between Stateful and Stateless firewalls.
- Example firewall rule: Allow TCP traffic from 192.168.1.10 on port 80; deny all others.
- Difference between Firewall, IDS (detects threats), and IPS (blocks threats).
- Hardware vs Software firewall:
- Hardware: Separate physical device, protects entire network.
- Software: Installed on a specific device, protects that device only.
- DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) usage in network security — adds an extra security layer for public-facing servers.
3. NAT (Network Address Translation)
Definition: Maps private IPs to public IPs for internet access.
Purpose: Conserves public IPs, enhances security by hiding internal IPs.
How it Works:
- Modifies IP headers in packets.
- Maintains a translation table for mappings.
Types:
- Static NAT: One-to-one mapping.
- Dynamic NAT: Temporary mapping from a pool.
- PAT: Multiple private IPs to one public IP using ports.
Use Cases:
- Home networks sharing a public IP.
- Hiding internal IP structure in enterprises.
- Load balancing and server mapping.
Interview Points:
- PAT vs. Static NAT: PAT uses ports; Static NAT is fixed.
- NAT in IPv6: Less needed due to large address space.
- Security: Provides obscurity, not a firewall.
4. SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security)
Definition: Cryptographic protocols for secure communication.
Purpose: Ensures confidentiality, integrity, authentication.
How it Works:
- Asymmetric cryptography for key exchange.
- Symmetric cryptography for data encryption.
- Validates server identity via CA-issued certificates.
Use Cases:
- Securing HTTPS websites.
- Encrypting emails (SMTPS, IMAPS).
- Protecting online transactions.
Key Terms:
- Certificate: Contains public key, server details.
- Cipher Suite: Encryption and authentication algorithms.
- TLS Versions: TLS 1.2, 1.3 (SSL deprecated).
Interview Points:
- TLS 1.3: Faster handshake, stronger security.
- Certificate Authorities: Role in trust chain.
- Attacks: MitM, SSL stripping.
5. Load Balancer
Definition: Distributes traffic across multiple servers.
Purpose: Ensures high availability, scalability, reliability.
How it Works:
- Forwards client requests based on algorithms.
- Monitors server health.
Types:
- Hardware: Physical devices (e.g., F5).
- Software: NGINX, HAProxy.
- Cloud: AWS ELB, Google Cloud Load Balancer.
Algorithms:
- Round-Robin: Sequential distribution.
- Least Connections: Fewest active connections.
- IP Hash: Based on client IP.
Use Cases:
- Scaling web applications.
- Ensuring uptime for critical services.
- Microservices architectures.
Interview Points:
- Layer 4 vs. Layer 7: Layer 4 (TCP/UDP) faster; Layer 7 (HTTP) smarter.
- Sticky Sessions: Maintains user session.
- Health Checks: Ensures healthy servers.
6. Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy
Beginner + Deep Understanding
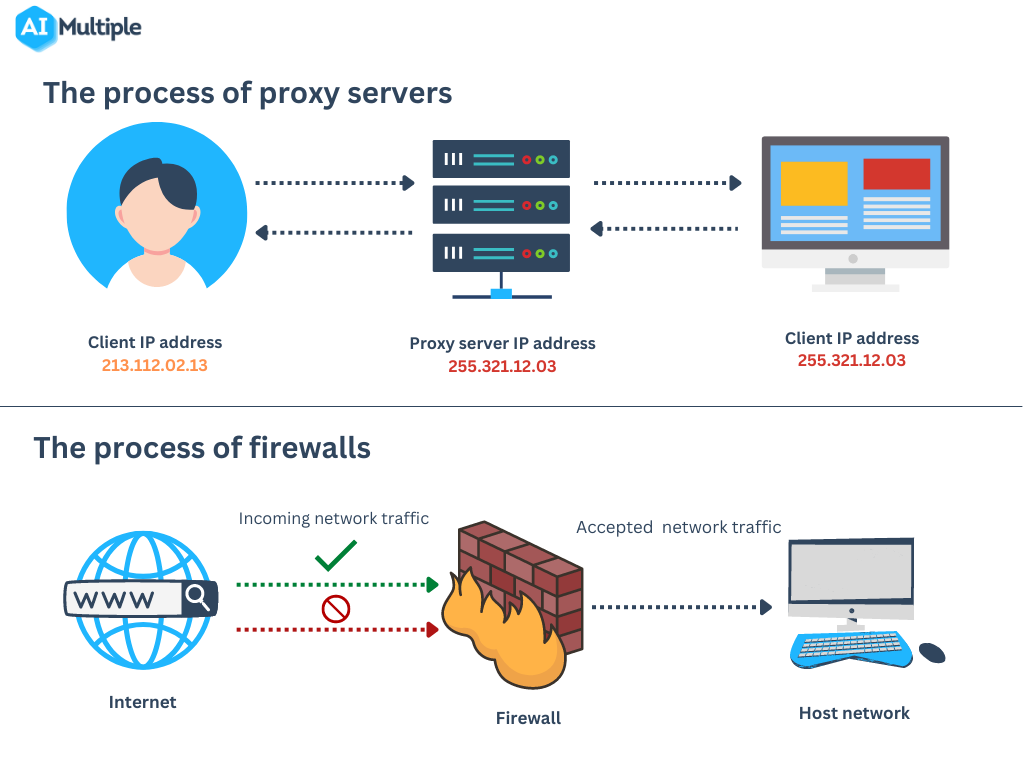
What is a Proxy? A proxy is like a middleman between you and the internet. Instead of talking directly to a website, you talk to the proxy, and it talks to the website for you.
Forward Proxy (Proxy): Sits between the client (your device) and the internet. It hides your identity from websites, can block certain sites, and can store (cache) content for faster loading. Example: Like a class monitor passing your note to the teacher without revealing who wrote it.
Reverse Proxy: Sits between the internet and backend servers. It hides the servers from the public, distributes traffic between them, and can handle security tasks like SSL. Example: Like a receptionist in a building directing visitors to the right department without revealing the office locations.
Key Difference: Forward Proxy protects the client’s identity. Reverse Proxy protects the server’s identity.
Proxy (Forward Proxy)
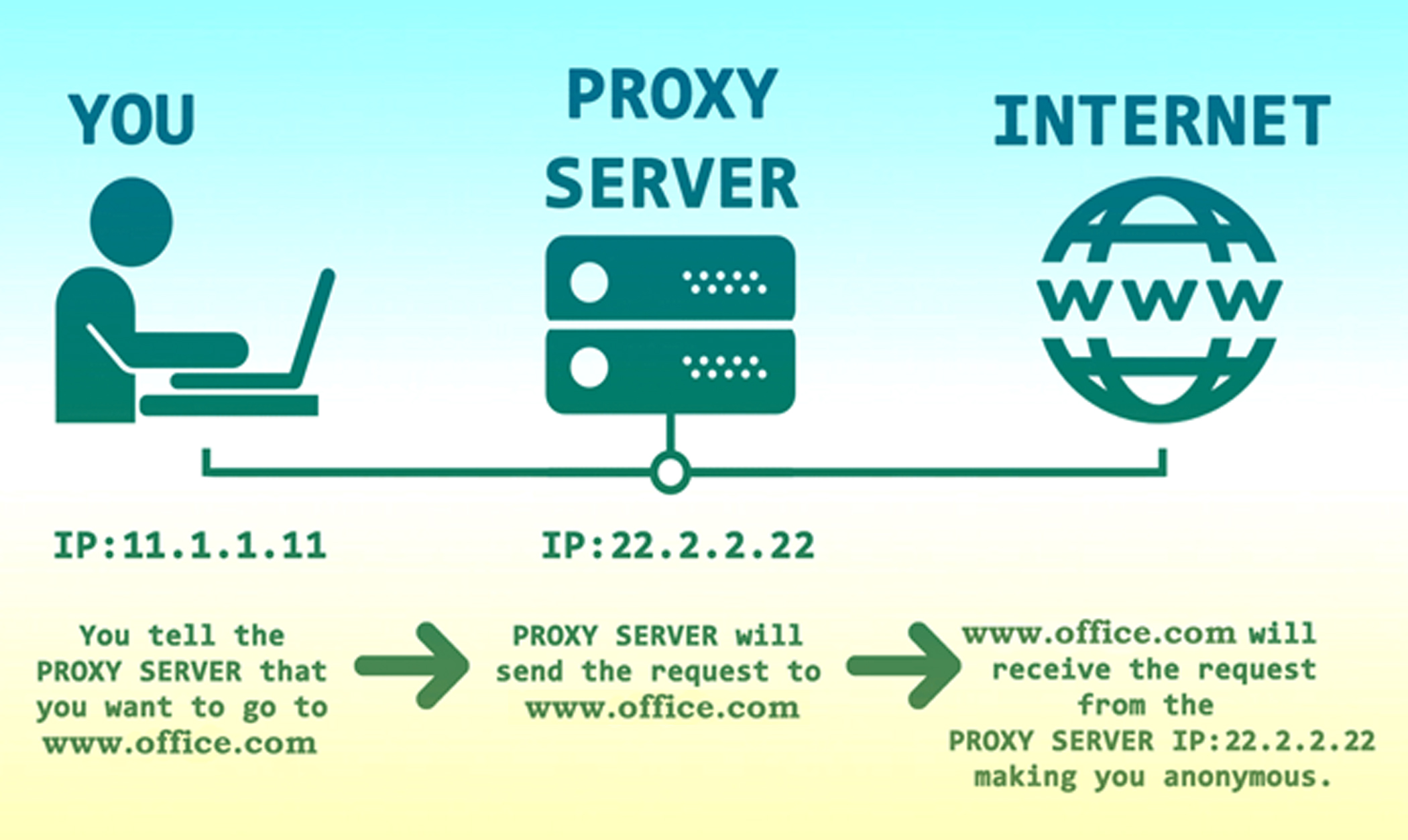
Definition: Server between client and internet, forwarding requests.
Purpose: Anonymity, content filtering, caching.
How it Works:
- Client sends request to proxy.
- Proxy forwards the request to the internet.
- Website sees proxy's IP, not the client’s IP.
Use Cases:
- Corporate internet monitoring.
- Bypassing geo-restrictions.
- Caching to reduce bandwidth.
Interview Points:
- Acts on behalf of client.
- Example: Squid Proxy.
Reverse Proxy

Definition: Server between internet and backend servers.
Purpose: Load balancing, security, SSL termination.
How it Works:
- Client sends request to reverse proxy.
- Reverse proxy decides which backend server should handle it.
- Client only sees reverse proxy’s IP, not the real server’s IP.
Use Cases:
- Load balancing web servers.
- SSL termination.
- Protecting backend servers.
Interview Points:
- Acts on behalf of server.
- Example: NGINX, AWS ALB.
Comparison
| Aspect | Proxy (Forward) | Reverse Proxy |
|---|---|---|
| Acts on Behalf of | Client | Server |
| Purpose | Anonymity, filtering, caching | Load balancing, security, caching |
| Location | Between client and internet | Between internet and servers |
| Hides | Client IP | Server IP |
| Examples | Squid, corporate proxies | NGINX, HAProxy, AWS ALB |
7. Debugging Tools
a. ping
Purpose: Checks connectivity via ICMP echo requests.
Use Case: Verifying server reachability.
Example: ping google.com
Interview Points:
- ICMP-based, may be blocked by firewalls.
- Use
-c(Linux) or-n(Windows) for packet count.
b. traceroute (tracert on Windows)
Purpose: Traces packet path to destination.
Use Case: Diagnosing routing issues.
Example: traceroute google.com
Interview Points:
- Uses ICMP (Windows) or UDP (Linux).
- Identifies packet loss or delays.
c. nslookup / dig
Purpose: Queries DNS for domain information.
Use Case: Troubleshooting DNS issues.
Examples: nslookup google.com, dig google.com +short
Interview Points:
digprovides detailed output.- Common records: A, CNAME, MX, NS.
d. netstat
Purpose: Displays connections, ports, routing tables.
Use Case: Identifying open ports.
Example: netstat -an
Interview Points:
- Flags:
-a(all),-n(numeric),-p(program). - Replaced by
ssin modern Linux.
e. ipconfig (Windows) / ifconfig (Linux)
Purpose: Displays network interface configuration.
Use Case: Troubleshooting IP issues.
Examples: ipconfig /all, ifconfig, ip addr
Interview Points:
ipconfig /release,/renewfor DHCP.ifconfigdeprecated; useip.
f. Wireshark
Purpose: Packet analyzer for traffic inspection.
Use Case: Debugging protocol issues, analyzing performance.
Interview Points:
- Filters:
ip.src == 192.168.1.1,http,tcp.port == 80. - Requires root/admin privileges.
- Useful for SSL/TLS handshake issues.
8. SSL/TLS Handshake Process
Definition: Establishes a secure connection between client and server.
Steps (TLS 1.3):
- Client Hello: Sends TLS versions, cipher suites, client random, SNI.
- Server Hello: Responds with TLS version, cipher suite, server random, certificate.
- Key Exchange: Uses Diffie-Hellman to generate session key; client verifies certificate.
- Authentication & Encryption: Confirms session key; uses symmetric encryption.
- Finished: Both send “Finished” message; secure communication begins.
Key Points:
- TLS 1.3: Faster (1-RTT), no deprecated ciphers.
- Certificates: Issued by CAs, validated via trust chain.
- Issues: Certificate mismatch, unsupported ciphers, MitM attacks.
Interview Points:
- TLS 1.2 vs. 1.3: 1.3 removes insecure ciphers, reduces latency.
- Session Resumption: Reuses session keys.
- Attacks: Downgrade attacks, certificate spoofing.
Interview Notes (Quick Review)
VPN
Definition: Secure tunnel for private communication.
Key Protocols: OpenVPN, IPSec, WireGuard.
Common Questions:
- How does a VPN ensure security?
- Site-to-site vs. remote-access VPN?
- What is split tunneling?
Firewall
Definition: Filters network traffic based on rules.
Types: Packet-filtering, stateful, application-layer, NGFW.
Common Questions:
- Stateful vs. stateless firewalls?
- How do firewalls handle encrypted traffic?
- What is a DMZ?
NAT
Definition: Maps private IPs to public IPs.
Types: Static NAT, Dynamic NAT, PAT.
Common Questions:
- PAT vs. Static NAT?
- Does NAT provide security?
- NAT in IPv6?
SSL/TLS
Definition: Protocols for secure communication.
Key Concepts: Certificates, cipher suites, handshake.
Common Questions:
- Explain TLS handshake.
- TLS 1.2 vs. 1.3?
- Mitigate MitM attacks in TLS?
Load Balancer
Definition: Distributes traffic across servers.
Types: Hardware, software, cloud-based.
Common Questions:
- Layer 4 vs. Layer 7?
- What are sticky sessions?
- How to handle server failures?
Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy
Proxy: Acts for clients (anonymity, filtering).
Reverse Proxy: Acts for servers (load balancing, security).
Common Questions:
- Proxy vs. Reverse Proxy differences?
- Use cases for reverse proxy?
- How does reverse proxy improve security?
Debugging Tools
Key Tools: ping, traceroute, nslookup/dig, netstat, ipconfig/ifconfig, Wireshark.
Common Questions:
- Troubleshoot “no connectivity” issue?
- Wireshark vs. ping?
- Verify DNS resolution with dig?
SSL/TLS Handshake
Steps: Client Hello, Server Hello, Key Exchange, Authentication, Finished.
Key Concepts: Certificates, session keys, cipher suites.
Common Questions:
- What happens during TLS handshake?
- TLS 1.3 improvements?
- Debug a failed TLS handshake?
Additional Interview Tips
- Be Concise: Explain in 2-3 sentences, elaborate if asked.
- Use Analogies: VPN as “secure tunnel,” Firewall as “gatekeeper.”
- Know Use Cases: Relate to real-world scenarios (e.g., VPN for remote work).
- Understand OSI Layers: Map tools/protocols (e.g., SSL at Layer 5/6).
- Practice Commands: Explain
ping,traceroute,digoutputs. - Security Focus: Highlight risk mitigation (e.g., SSL prevents eavesdropping).